Description
HOMOLEPTIC VS HETEROLEPTIC POSS® ADDITIVES
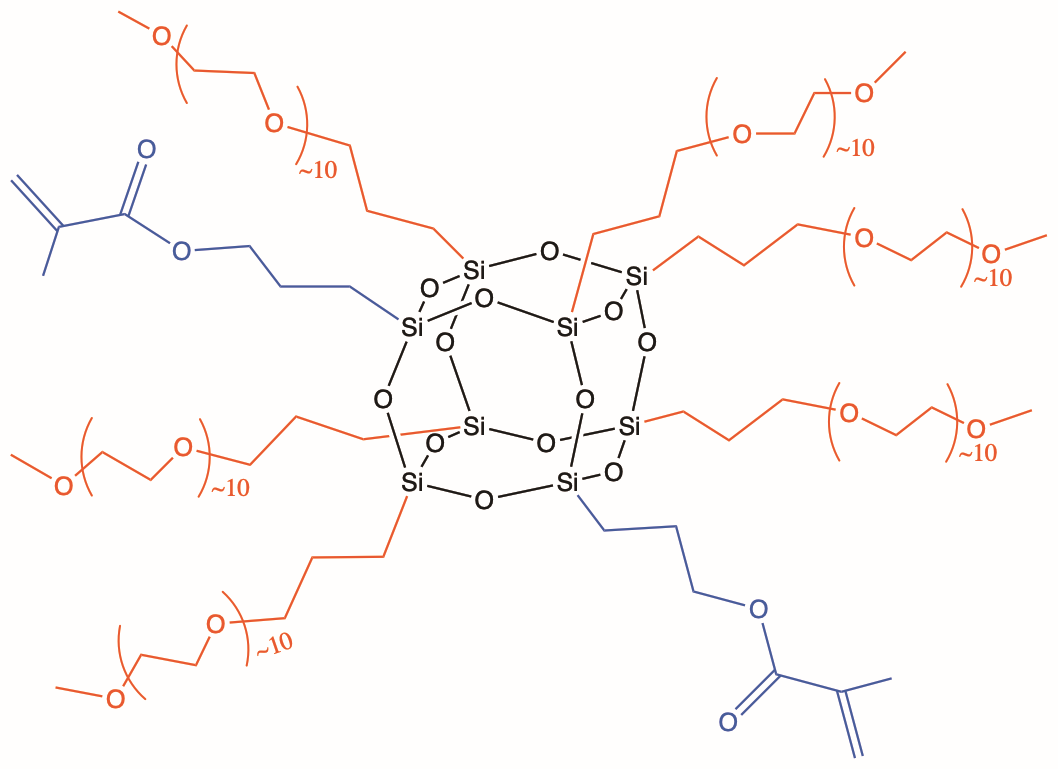
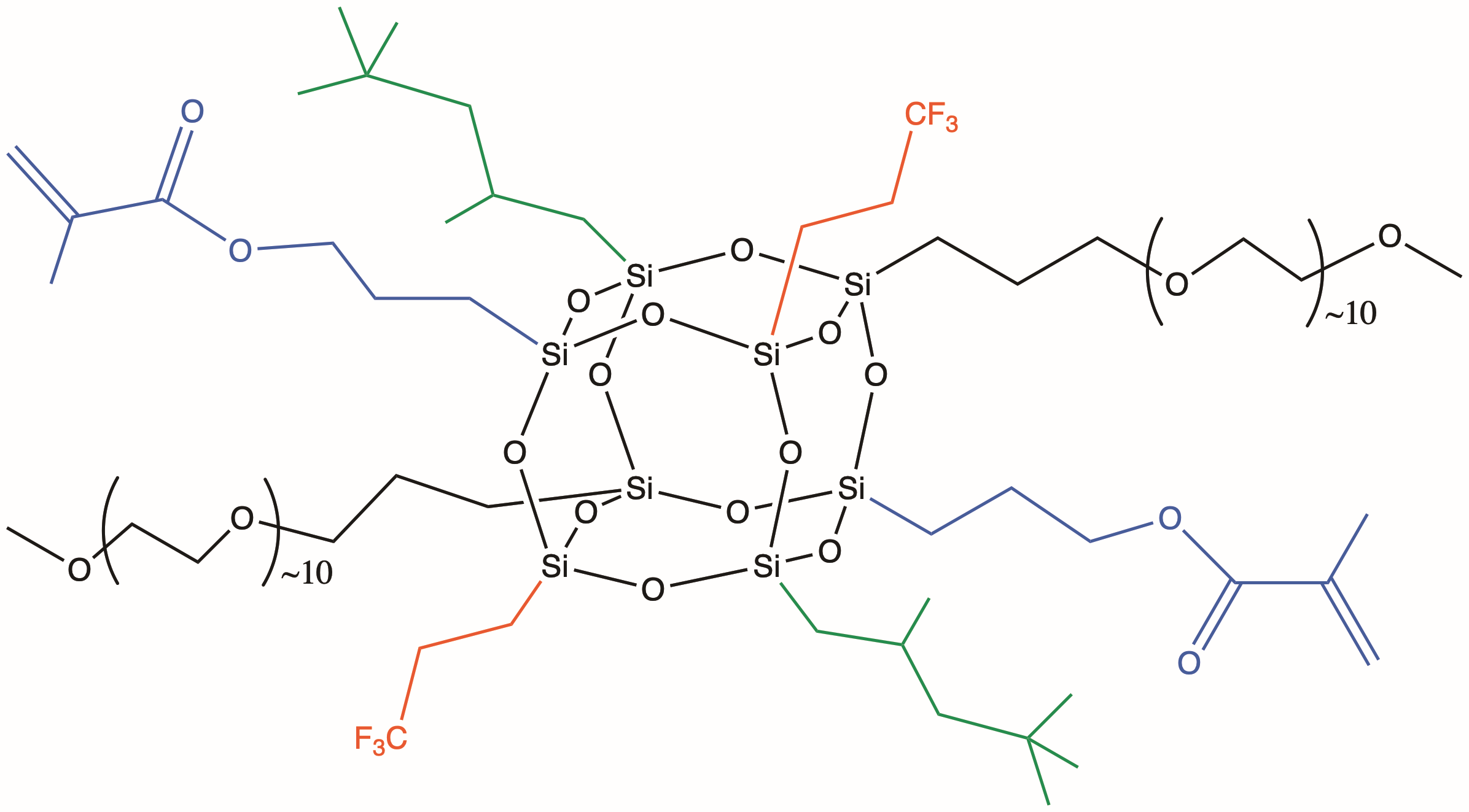
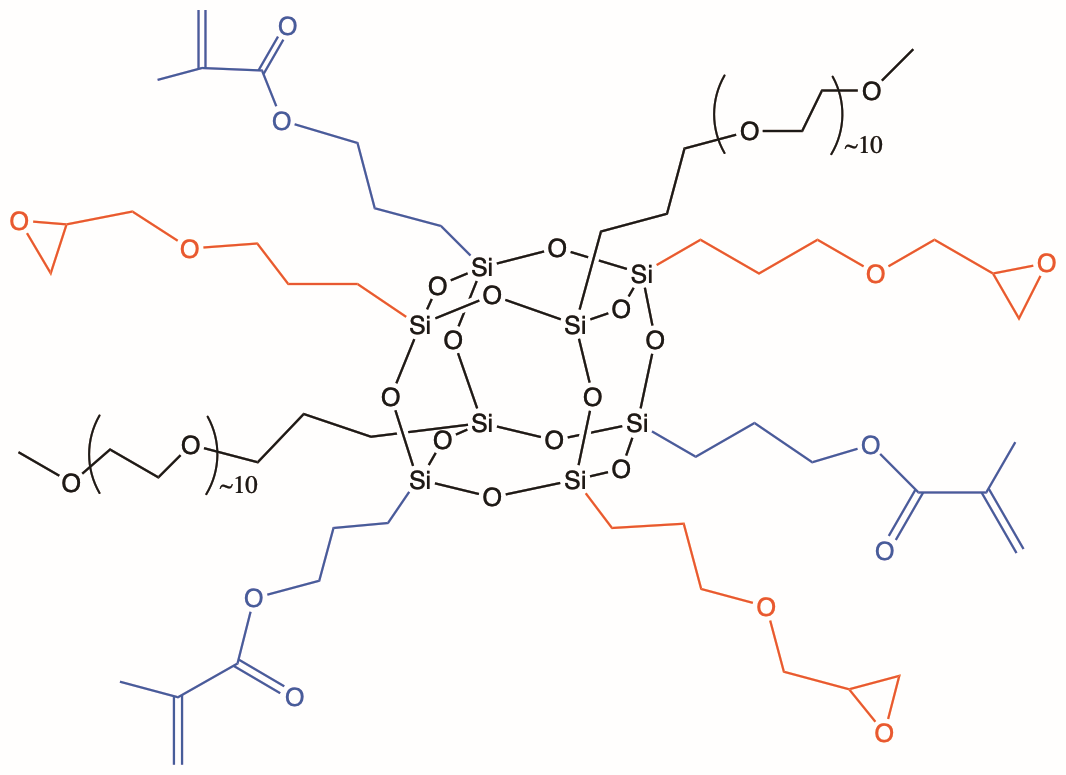
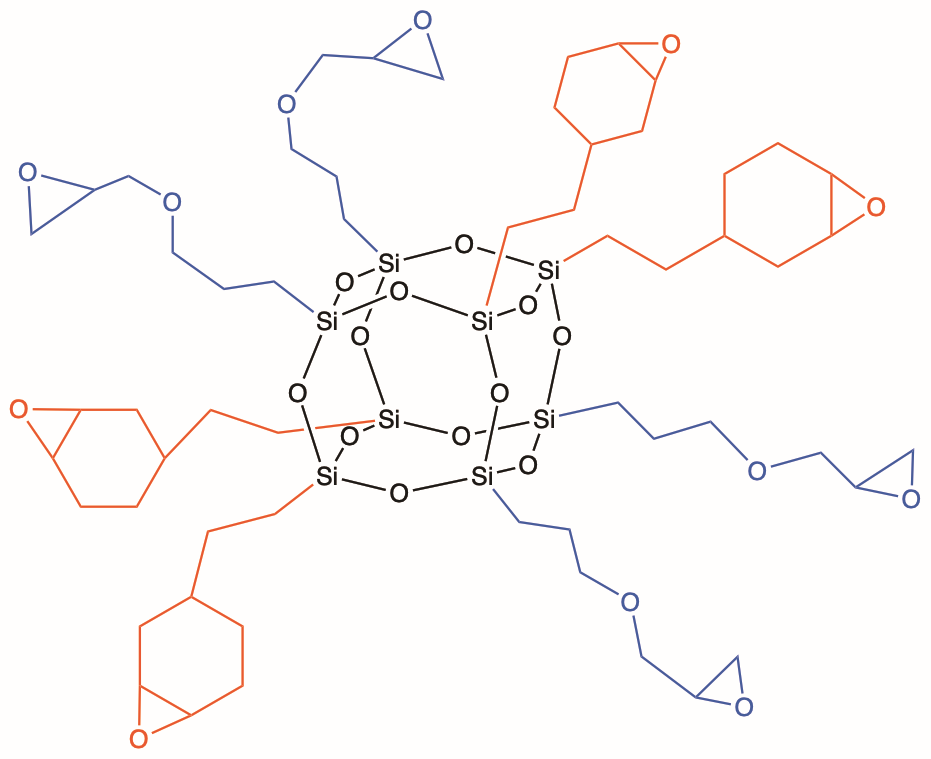
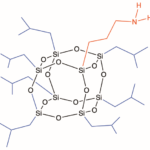
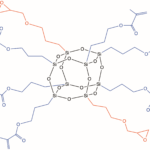
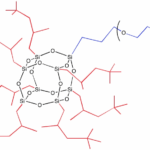
Heterolepetic cages (HC) are the third generation of POSS® additives. They are advantageous because they provide a statistically random distribution of two or more organic groups around the cage core. Especially unique to heteroleptics, is their ability to incorporate disparate organic functionalities together on the same cage. This new versatility allows HC POSS additive to serve as compatibilizers in addition to providing an envelope of effects. The example shown below illustrates the combination of glycidyl and methacryl groups onto a heteroleptic cage. *Multiple primary reactive groups, can be combined with multiple secondary “effect” groups on heterocages.
Send custom requests to info@hybridplastics.com
All HC POSS® still retain the cage structure that enables them to be formulated in the same manner as organic-additives into thermoset, elastomer, and thermoplastic formulations. The cage core size in HC POSS is a distribution of eight, ten and twelve which renders most HC POSS to be liquids as opposed to solids. The distribution of organic groups follows mathematical combinatorics.
ADVANTAGES: Ideal for coatings that can benefit from primary reactivity and secondary effects (dispersion, gloss, leveling, compatibilization etc.). HC POSS eliminate the need for use of multiple additives thus simplifying formulations.
APPLICATIONS: Adhesives coatings, dispersion and reactive rheological diluents . Tie-layers, dual-uv cure (cationic + free radical) replacing oven processing, toughening at low loadings.
The suggested loading levels for HC POSS are 0.5-3 wt% relative to resin.
| Primary Reactivity “R” group | Name | Effect |
| Methacryloxypropyl | Fast UV, thermal, addition cure, vulcanization, rheological diluency, adhesion/reaction to coupling agents | |
| Acryloxypropyl | Faster UV, thermal, addition cure, vulcanization, rheological diluency, adhesion/reaction to coupling agents | |
| Alpha Acryloxy | Fastest UV, thermal, addition cure, vulcanization, adhesion to coupling agents | |
| Glycidyl | Cationic UV, thermal cure adhesion, coupling agent adhesion, modest dispersion | |
| Cyclohexylethylepoxy | Cationic UV, thermal cure, coupling agent adhesion, overall adhesion promoter | |
| Ethylnorbornene | ROMP, thermal cure, vulcanization, toughener for hydrosilylation cures relative to the vinyl functionality | |
| Vinyl | ADMET, thermal cure, vulcanization, hydrosilylation cure |
| Secondary Effect “R” group | Name | Effect |
| MethoxyPEG10 | Wetting, dispersion, levelling, adhesion, gloss, water dispersion, bio-issue compatibilization | |
| Phenyl | Compatibilization with aromatics, high temp stability. | |
| Iso-octyl | Gloss, hydrophobicity, aliphatic compatibilization, rheological diluent, plasticization | |
| Iso-butyl | Hydrophobicity, aliphatic compatibilization, modest reinforcement, modest plasticization | |
| Trifluoropropyl | Similar to i-butyl, compatibilization of fluorinated additives. | |
| Methyl | Low carbon efficiency. |
Links to current heterocage offerings are provided below.